Jump To: Support > KB > NetManager > Firewalling > NAT
NAT (Network Address Translation)
NAT allows you to hide a whole private network (which may contain thousands of machines) behind a single IP address. This has a number of benefits:
- If your Internet connection (and thus external IP address) changes, you do not need to re-configure any machines except the NetManager.
- All internal machines are protected from access from the outside
- You can easily filter outbound traffic from internal machines using firewalling.
- You can have many more internal machines than your ISP have allocated you IP addresses for. Some LEA-provided school connections may have only 256 addresses. Real Internet connections have even fewer (perhaps only 1 or 5).
NAT is easily enabled in webadmin by going to Network > NAT
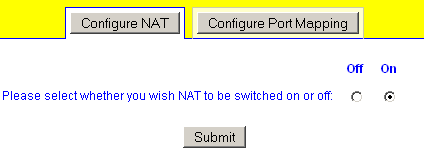
To allow access to internal machines from outside, you will need to use Port Mapping.
Advanced settings
If NAT is enabled, the default action is to determine the external network interface (based on the default gateway that is set) and then map through all other interfaces to the first IP address on that external interface. Internally, this create a lists of interface pairs to map between. For example, if wm2 is your external interface and wm0 and wm1 are internal, this will generate a setting of wm0>wm2 wm1>wm2. You can override this automatically-created list by setting nat_advanced. For instance, you might not want to map the networks attached to wm1 (i.e. you don't want them to have any Internet access).
The syntax is a space-separated list of from>to rules. There are currently two rule formats understood:
from-interface>to-interface, e.g.wm0>wm2packet-matching-rules>IP-address. Packets that match the specified rules will be mapped to the IP address given. Rules are given as a comma-separated list of flags. Valid flags are:src=- source IP address(es) (i.e. client IP). Can include netmask, e.g.src=192.168.1.0/24dst=- destination IP address(es) (i.e. what is being talked to). Can include netmask, e.g.dst=80.71.28.0/26port=- destination port number (i.e. what service is being talked to). Can be used to map particularly services to a different external IP address, e.g.port=80
nat_advanced="wm0>wm2 src=192.168.1.123,port=80>100.101.102.104"
If we assume the main IP address on wm0 is 192.168.1.0/24 and the main IP address on wm2 is 100.101.102.103 then all traffic from 192.168.1.0/24 (e.g. client 192.168.1.1) will go out from IP address 100.101.102.103, except for client 192.168.1.123 speaking http (port 80) which will go out on 100.101.102.104